1 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所瞬态光学与光子技术国家重点实验室,陕西 西安 710119
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3 Laboratory of Applied Computational Imaging,Centre Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications,Institut National de la Recherche Scientifique,Université du Québec,Québec J3X1P7,Canada
高速成像技术在物理、化学、生物医学、材料科学及工业等众多领域扮演着十分重要的角色。受电荷存储和读取速度的限制,基于电子成像器件的数码相机成像速度难以进一步提高。近年来,随着成像新技术的发展,超高速和极高速光学成像的性能已得到显著提升,具备更高的时间分辨率、空间分辨率及更大的序列深度等。介绍高速成像技术的发展历程,根据成像方式,将近年来具有代表性的新型超高速和极高速光学成像技术分为直接成像和编码计算成像两个类别。分别介绍和讨论各种新型超高速和极高速光学成像技术的概念和原理,并比较各自的优缺点。最后,对这一领域的发展趋势和前景进行展望。本文旨在帮助研究者系统了解超高速和极高速光学成像技术的基本知识、最新研究发展趋势和潜在应用,为该领域科学研究提供参考。
高速成像 超高速成像 极高速成像 时间分辨率 空间分辨率 序列深度 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(2): 0211020
1 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所瞬态光学与光子技术国家重点实验室,陕西 西安 710119
2 西安电子科技大学物理学院,陕西 西安 710071
定量相位显微成像在工业检测、生物医学和光场调控等领域具有重要的应用价值。常用的定量相位显微成像技术通过干涉的方法来获取相位的定量分布,干涉装置的稳定性、光学衍射极限的限制、相位再现时的解包裹问题、激光照明下的相干噪声,以及动态观测过程中的样品离焦等因素都会影响定量相位显微成像的分辨率和精度。本文围绕高精度定量相位显微成像中的上述关键问题展开研究,通过构建物参共路的同步相移数字全息显微结构实现稳定的实时测量;采用结构光照明的超分辨相位成像方法实现对微小物体的超分辨相位成像;利用双波长照明将纵向无包裹相位测量范围扩大到微米量级;使用低相干LED照明解决相干噪声问题;提出了基于结构光照明和双波长照明的数字全息显微自动调焦方法,可以满足对不同类型样品的长时间跟踪观测。
定量相位显微成像 物参共路 结构光照明 相位解包裹 自动调焦
光子学报
2023, 52(11): 1110004
光子学报
2022, 51(11): 1118001
光子学报
2021, 50(11): 1123001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an 710119, China
2 Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
3 Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao), Qingdao 266200, China
Dual-wavelength in-line digital holography (DIDH) is one of the popular methods for quantitative phase imaging of objects with non-contact and high-accuracy features. Two technical challenges in the reconstruction of these objects include suppressing the amplified noise and the twin-image that respectively originate from the phase difference and the phase-conjugated wavefronts. In contrast to the conventional methods, the deep learning network has become a powerful tool for estimating phase information in DIDH with the assistance of noise suppressing or twin-image removing ability. However, most of the current deep learning-based methods rely on supervised learning and training instances, thereby resulting in weakness when it comes to applying this training to practical imaging settings. In this paper, a new DIDH network (DIDH-Net) is proposed, which encapsulates the prior image information and the physical imaging process in an untrained deep neural network. The DIDH-Net can effectively suppress the amplified noise and the twin-image of the DIDH simultaneously by automatically adjusting the weights of the network. The obtained results demonstrate that the proposed method with robust phase reconstruction is well suited to improve the imaging performance of DIDH.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(12): 12002501
1 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所瞬态光学与光子技术国家重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710119
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
生物医学研究的发展对光学显微成像的性能,如空间分辨率、成像速度、多维度信息、成像质量等提出了更高的要求。光片荧光显微采用一个薄片光从侧面激发样品,在正交方向探测成像,具有快速三维层析成像和对样品光漂白和光毒性小的优点,是活体生物样品长时间显微观测的理想工具。本文介绍了光片荧光显微成像技术的基本原理及其主要特点;综述了光片荧光显微面临的主要技术问题,以及为解决这些问题而发展出的新原理、新思路和新方法;例举了光片荧光显微成像技术在细胞生物学、发育生物学和神经科学等领域的应用;讨论了该技术的发展趋势及前景。该研究旨在帮助研究者系统了解光片荧光显微成像技术的基本知识、最新研究发展趋势和潜在应用,为该领域科学研究提供参考。
显微 荧光显微 光片照明 三维成像 生物医学成像 激光与光电子学进展
2020, 57(10): 100001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an 710119, China
2 Engineering and Surface Metrology Laboratory, National Institute of Standards, Tersa St., El haram, El Giza, Egypt
3 Division of Mechanical System Engineering, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju 561-756, Republic of Korea
We present a Fizeau interferometer using a microscopic objective as a tool for surface contouring without the need for a numerical lens for reconstruction. The interferometer is associated with a telescope system to feature the object with collimated light. The experiment is conducted on two objects possessing different step heights. The phase maps from the captured off-axis holograms are calculated numerically, which allows us to deduce the contours of the objects. The great advantages of the presented technique are that it can be done in real time and there is no need for numerical lenses for micro-objects reconstruction.
070.6110 Spatial filtering 100.5090 Phase-only filters 170.0180 Microscopy 180.0180 Microscopy Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(10): 100701
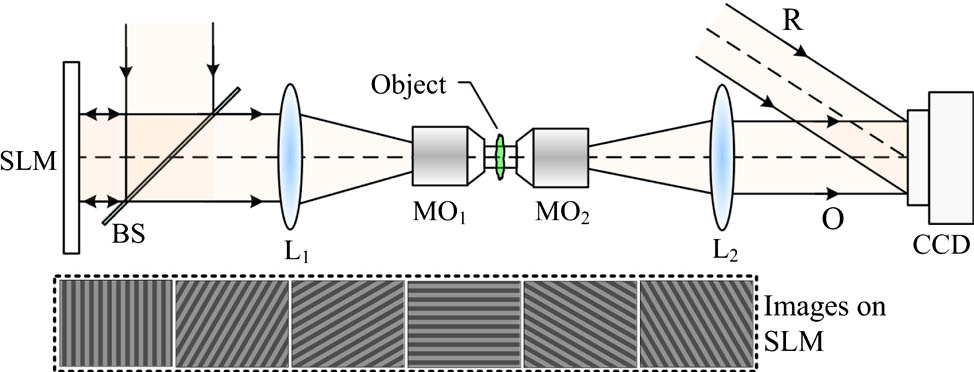
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an 710119, China
2 Institut fur Technische Optik, Universitat Stuttgart, Pfaffenwaldring 9, 70569 Stuttgart, Germany
3 Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, Clemson-MUSC Bioengineering Program, Charleston, South Carolina 29425, USA
When structured illumination is used in digital holographic microscopy (DHM), each direction of the illumination fringe is required to be shifted at least three times to perform the phase-shifting reconstruction. In this paper, we propose a scheme for spatial resolution enhancement of DHM by using the structured illumination but without phase shifting. The structured illuminations of different directions, which are generated by a spatial light modulator, illuminate the sample sequentially in the object plane. The formed object waves interfere with a reference wave in an off-axis configuration, and a CCD camera records the generated hologram. After the object waves are reconstructed numerically, a synthetic aperture is performed by an iterative algorithm to enhance the spatial resolution. The resolution improvement of the proposed method is proved and demonstrated by both simulation and experiment.
Digital holography Holographic interferometry Interference microscopy Phase measurement Photonics Research
2014, 2(3): 03000087





